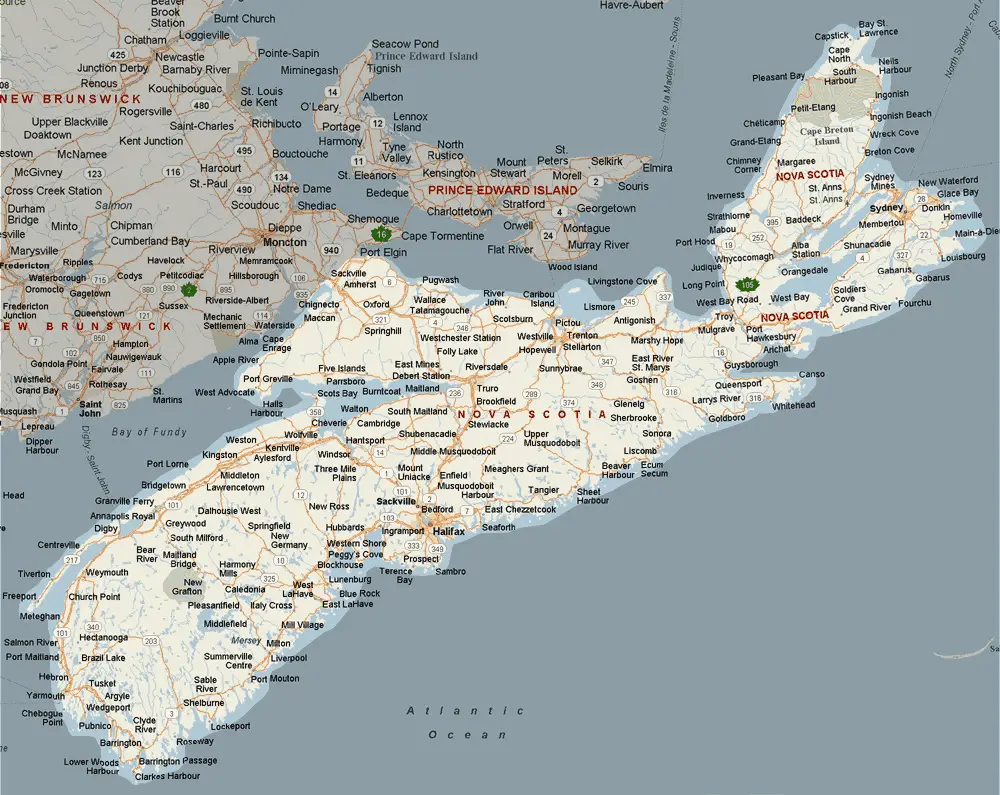
PPT Plant Cells PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2349840
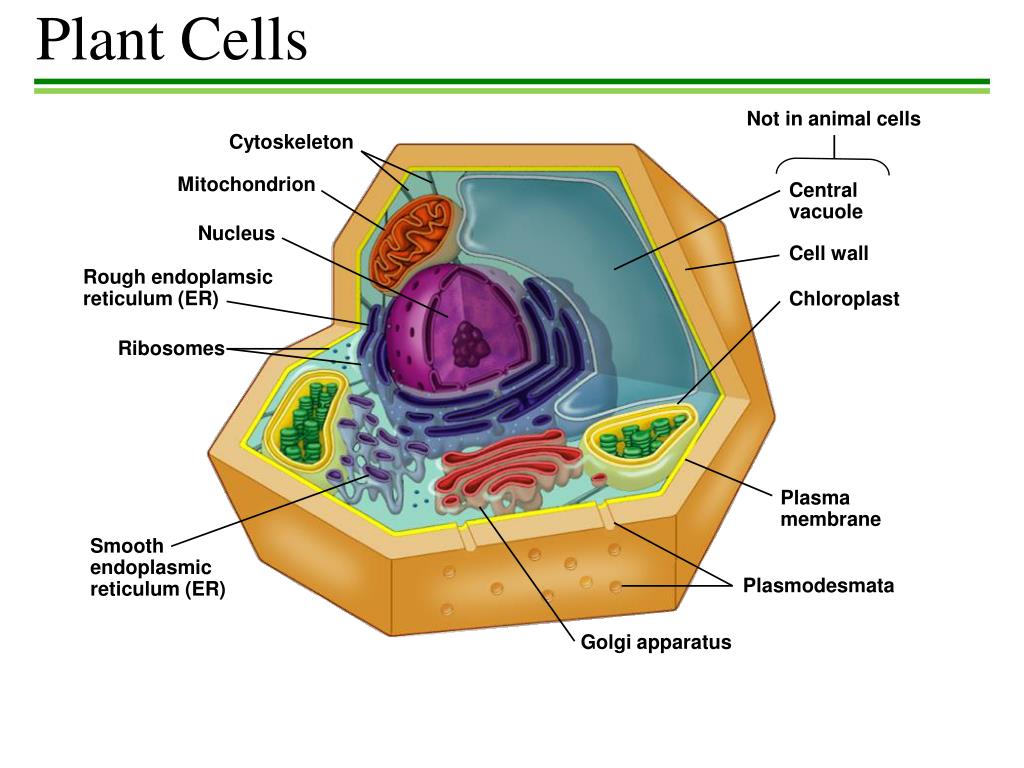
Figure \(\PageIndex{12}\): Phloem in a cross section of a Cucurbita (squash) stem, magnified at 400X. Each wide sieve-tube cell has a small, dark companion cell associated with it. (The companion cells are dark because each contains a nucleus.) The cross section cut exactly in between two sieve tube elements in some cases, revealing the sieve.
FileSimple diagram of plant cell (en).svg Wikimedia Commons
.svg/1280px-Simple_diagram_of_plant_cell_(en).svg.png)
BIOL 221 - Concepts of Botany Fall 2010. Plant Cells, Tissues and Meristems. Figure 1. Plant stem cross-sections depicting various tissue and cell types. A. Introduction to Plant Cells. Cells are the structural and functional units of living organisms. The plant cell has essentially everything that an animal cell does AND MORE.
Diagrams of Plant Cell 101 Diagrams

chloroplast. vacuole. turgor. sclerenchyma cell. vessel cell. plant cell, the basic unit of all plants. Plant cells, like animal cells, are eukaryotic, meaning they have a membrane-bound nucleus and organelles. The following is a brief survey of some of the major characteristics of plant cells. For a more in-depth discussion of cells, see cell.
Learn the Different Types of Plant Cells
/cutaway-drawing-of-a-eukaryotic-plant-cell--141482967-5a0228abbeba33001ae74b56.jpg)
All plant cells have what is called a primary cell wall described in chapter 3. It is composed of cellulose microfibrils imbedded in a matrix of hemicellulose and pectins, molecules that bind cellulose microfibrils to each other and also absorb water, forming a gel.. It is difficult to distinguish the two cell types in cross-section. However.
plant cell structure large Radical Botany
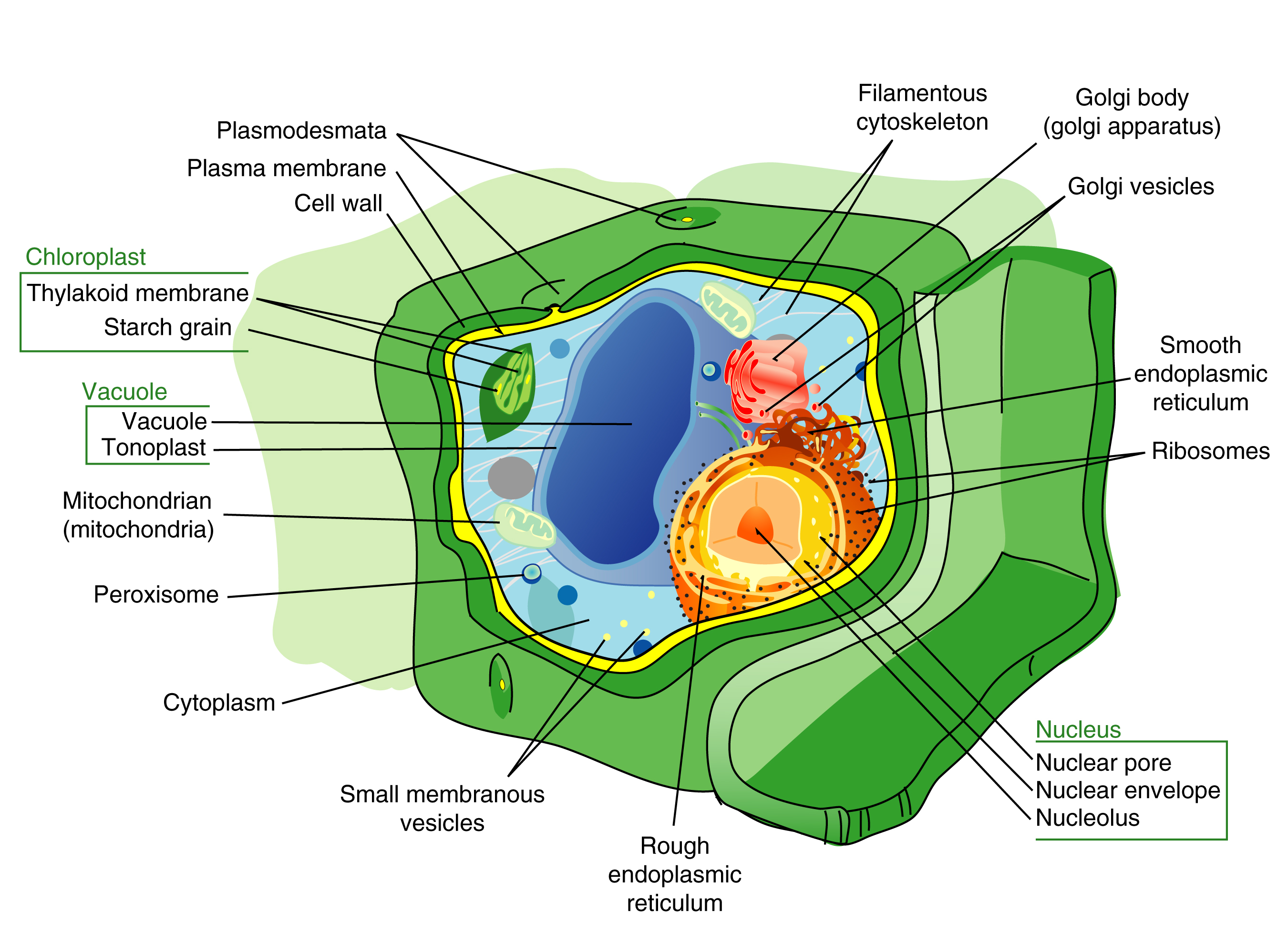
Figure 1. Plant cross sections depicting various tissue and cell types. (Photo Atlas: Figures 1.3, 1.5, 1.6, 1.10 Æ 1.25, 1.29) A. Introduction to Plant Cells: CELLS are the structural and functional units of living organisms. In multicellular organisms, groups of cells similar in structure and function are known as TISSUES. In
Why do plant cells need a cell wall and animal cells do not?
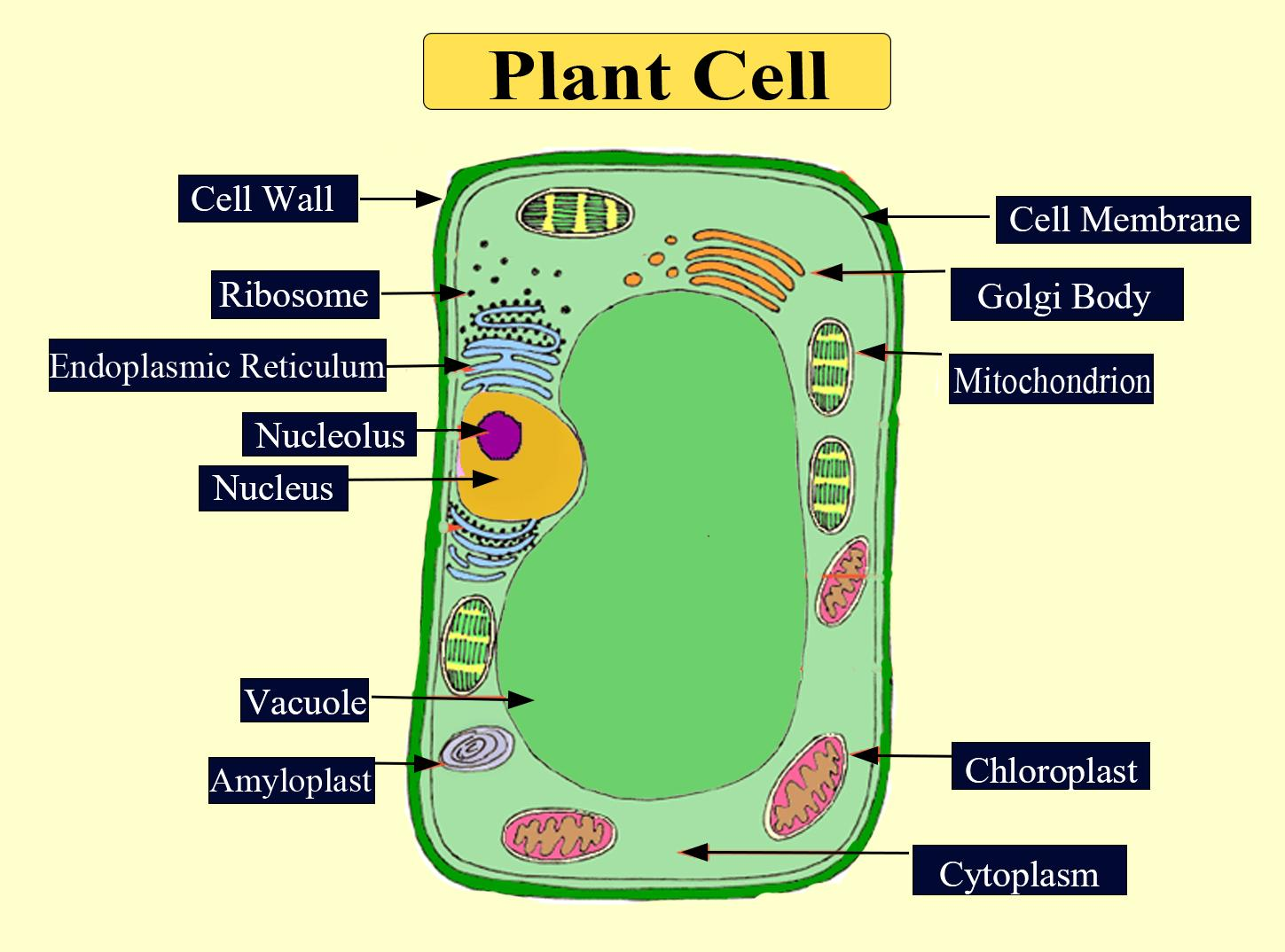
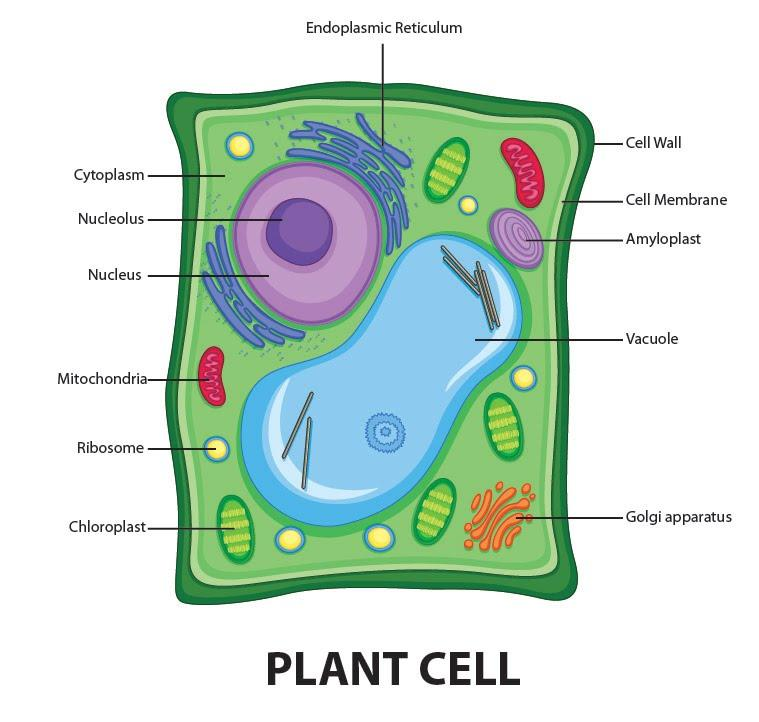
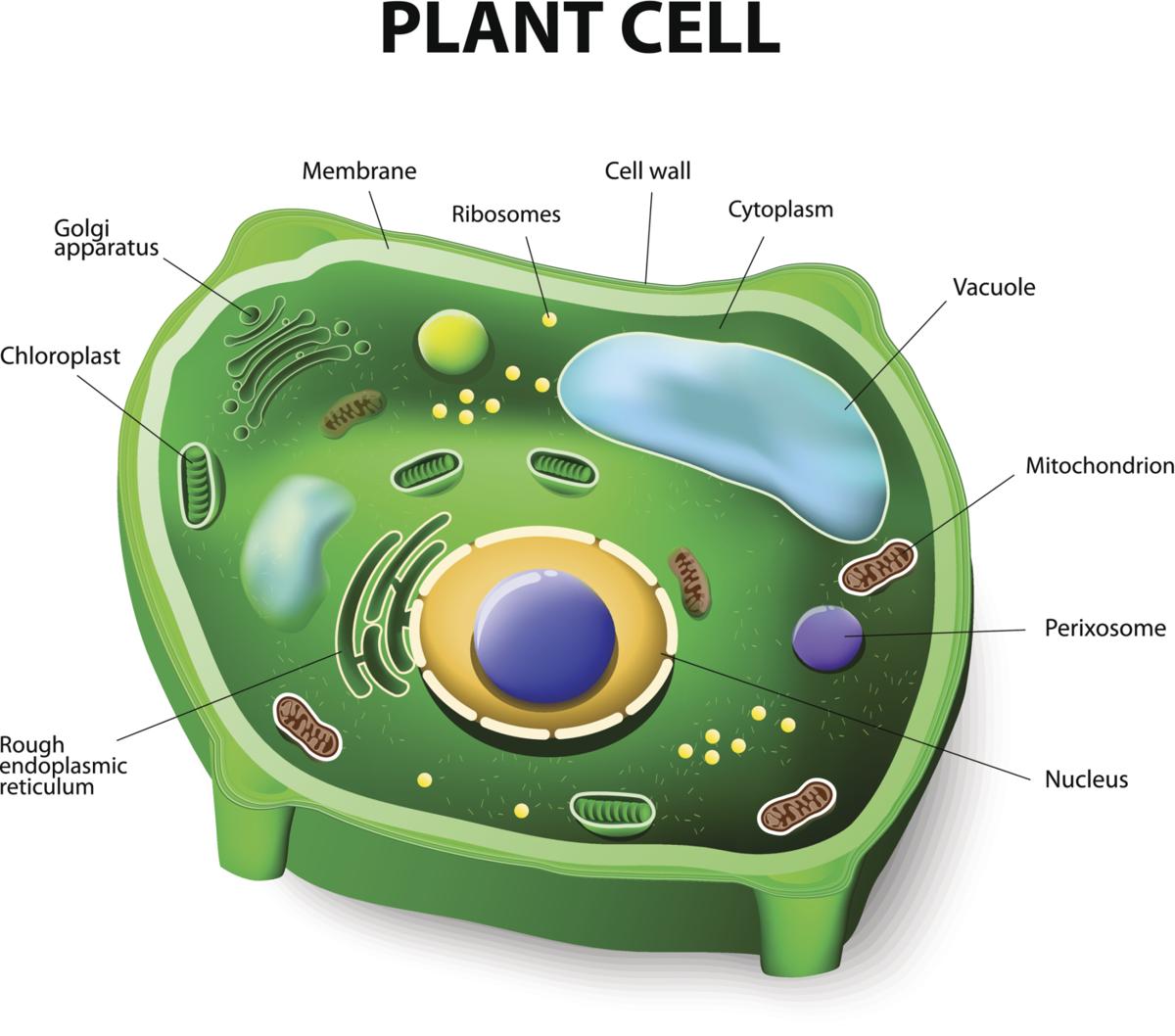
Distinguishing characteristics of a plant cell are its cell wall, chloroplasts, and large vacuole. A plant cell is the basic building block of a plant. Plant cells, like all eukaryotic cells, contain a nucleus and other organelles, each with its distinct functions. However, plant cells also possess unique components that differentiate them from.
Structure des cellules végétales. Diagramme vectoriel. Anatomie d'une cellule biologique avec

Figure 10.1.5 10.1. 5: A micrograph of a cell nucleus. The nucleolus (A) is a condensed region within the nucleus (B) where ribosomes are synthesized. The nucleus is surrounded by the nuclear envelope (C). Just oustide the nucleus, the rough endoplasmic reticulum (D) is composed of many layers of folded membrane.
crosssection of plant cell inspiration things. Microscopic photography, Plant cell

cross-section of a plant cell. Get a hint. cell wall. Click the card to flip 👆. outer layer of plant cells and gives support and protection. Click the card to flip 👆. 1 / 15.
Plant Cell Parts and Structure

Definition. Plant cells are the basic unit of life in organisms of the kingdom Plantae. They are eukaryotic cells, which have a true nucleus along with specialized structures called organelles that carry out different functions. Plant cells have special organelles called chloroplasts, which create sugars via photosynthesis.
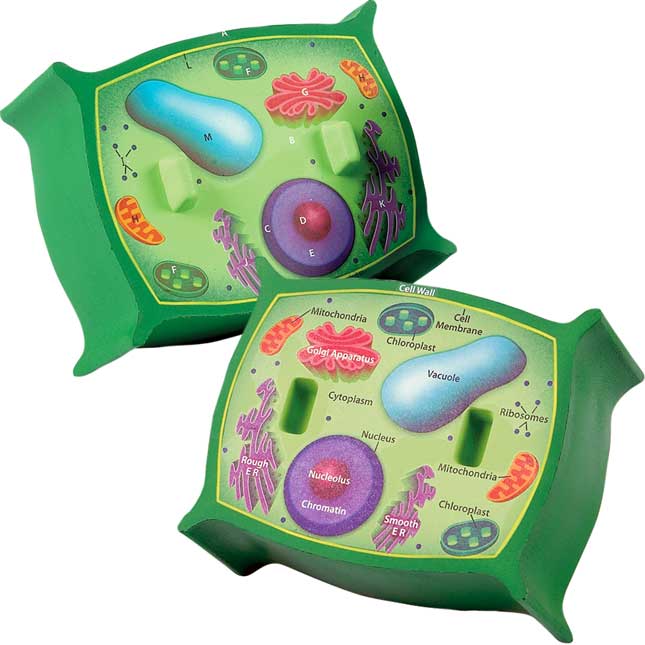
Draw a welllabelled diagram of a plant cell.
First of all, both plants and animal cells have a cell membrane. A cell wall is more of a structural layer outside the cell membrane, mainly composed of cellulose but has other things, causing rigidity. Animals are fleshy and malleable because they lack the rigidity caused by a cell wall.
Pin on GCSE Science paper 1

In plant cells, ATP is produced in the cristae of mitochondria and chloroplasts. cell membrane - the thin layer of protein and fat that surrounds the cell, but is inside the cell wall. The cell membrane is semipermeable, allowing some substances to pass into the cell and blocking others. A thick, rigid membrane that surrounds a plant cell.
labeled chloroplast diagram Zen Lace

Functions of the plant cell (plasma) membrane. In-plant cells the cell membrane separated the cytoplasm from the cell wall. It has a selective permeability hence it regulates the contents that move in and out of the cell. It also protects the cell from external damage and provides support and stability to the cell.
Plant Cell Parts and Structure

3. DNA, the heredity information of cells, which can be found in a nucleus of eukaryotic cells and the a nucleoid region of prokaryotic cell. 4. ribosomes, or protein-synthesizing structures composed of ribosomes and proteins. These structures can be found on the image of the plant cell (Figure 3.1.2.1 3.1.2. 1 ).
Cross section of a plant stem under a microscope. Biology art, Plant cell, Bio art

Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\): Parenchyma cells in plants: The stem of common St John's Wort (Hypericum perforatum) is shown in cross section in this light micrograph. The central pith (greenish-blue, in the center) and peripheral cortex (narrow zone 3-5 cells thick, just inside the epidermis) are composed of parenchyma cells.
A Brief Comparison of Plant Cell Vs. Animal Cell Biology Wise
Cells seen in a plant stem cross-section (Source: RolfDieterMueller [CC BY 3.0] via Wikimedia Commons). Image - Text Version. Shown is a colour photograph of a thinly sliced plant stem, through a microscope. The stem is sliced to show all the cells inside its thickness. The result is a large, intricately patterned circle that stretches across a.
Cross Section Of A Plant Cell slidesharetrick
Plant cells are the cells present in green plants, photosynthetic eukaryotes of the kingdom Plantae.. Cross section of a leaf showing various plant cell types . Sclerenchyma. Sclerenchyma is a tissue composed of two types of cells, sclereids and fibres that have thickened,.
.